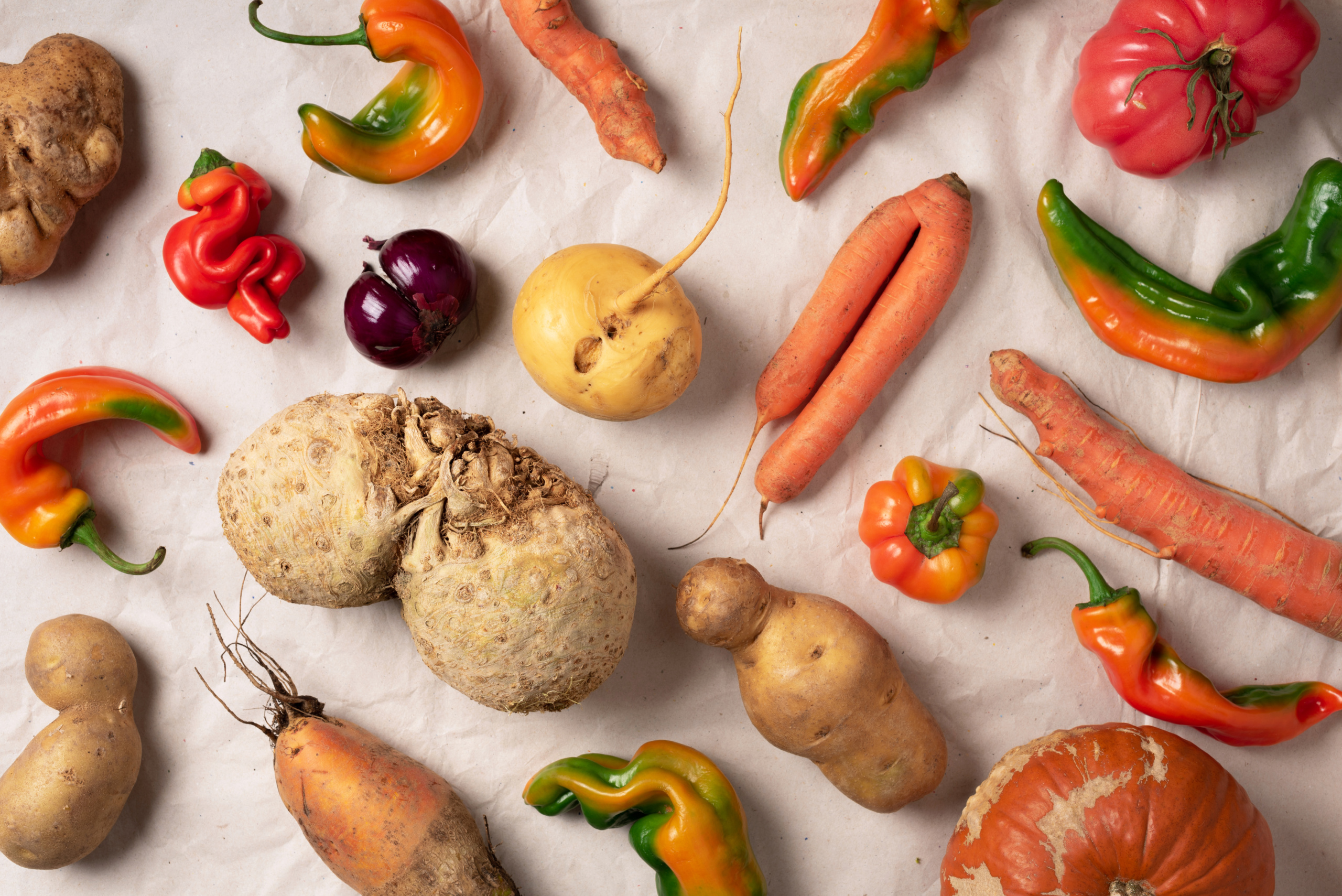
When it comes to healthy eating, starchy vegetables often spark debate. Are they a nutritious choice, or should they be avoided? Let’s dive into the world of starchy vegetables and discover how they can fit into a balanced diet.
What Are Starchy Vegetables?
Starchy vegetables are those that contain a higher amount of carbohydrates compared to non-starchy varieties. Common examples include:
- Potatoes
- Sweet potatoes
- Corn
- Peas
- Butternut squash
- Carrots
These vegetables are often seen as “comfort foods” and can be quite filling, making them popular choices for meals and snacks.
Nutritional Benefits
- Rich in Nutrients: Starchy vegetables are packed with essential vitamins and minerals. For instance, sweet potatoes are high in vitamin A, while peas provide a good source of vitamin C and fiber.
- Good Source of Energy: The carbohydrates found in starchy vegetables are an important source of energy. This can be particularly beneficial for active individuals and athletes who need fuel for their daily activities.
- Dietary Fiber: Many starchy vegetables contain fiber, which supports healthy digestion and can help you feel full longer. Fiber is also beneficial for maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
- Versatile and Delicious: Starchy vegetables can be enjoyed in a variety of ways—mashed, roasted, in soups, or as a side dish. Their natural sweetness and hearty texture make them a favorite in many cuisines.
Balancing Starchy Vegetables in Your Diet
While starchy vegetables offer many benefits, moderation is key. Here are some tips for incorporating them into your diet:
- Pair with Non-Starchy Veggies: Balance your plate by filling half of it with non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, and bell peppers. This adds variety and nutrients while keeping the overall carbohydrate content in check.
- Watch Portion Sizes: Being mindful of portion sizes can help you manage your carbohydrate intake. A serving of starchy vegetables is typically about half a cup cooked.
- Choose Whole Forms: Whenever possible, opt for whole or minimally processed forms of starchy vegetables. For instance, roasted sweet potatoes are a better choice than sweet potato fries.
- Consider Your Activity Level: If you lead an active lifestyle, starchy vegetables can be a great source of energy. On less active days, you might want to focus more on non-starchy options.
So, are starchy vegetables okay to eat? Absolutely! They can be a nutritious and delicious part of your diet when consumed in moderation and paired with a variety of other foods. By including starchy vegetables alongside plenty of non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, you can enjoy a well-rounded and satisfying diet. Embrace the versatility and flavor of starchy vegetables—they’re here to stay!