
Whether it’s a dull ache, a sharp sting, or just that annoying “full” feeling, ear pain can appear out of nowhere. Sometimes the ear itself is the source of the issue, but other times the pain is actually “borrowed” from another part of the body, such as the jaw or throat. Finding the appropriate relief requires an understanding of the underlying cause of the discomfort. Let’s go over ten typical causes of ear pain and how to address them.
1. The Common Cold

It’s possible that your stuffy nose is causing more than just sniffles. The Eustachian tube, a tiny passageway that runs from the back of your nose to your middle ear, can become irritated by a cold. Ear pain, fullness, popping sounds, and occasionally even ringing are caused by the pressure that builds up when it swells.
2. Sinus Infections

Infection-induced sinus swelling can obstruct the Eustachian tube and cause ear pain. Alongside the earache, you might also experience headaches, congestion, or pressure in your face.
3. Allergies

In addition to making you sneeze, seasonal allergies can cause swelling in the tissues of your sinuses and nose. Particularly during allergy season, you may experience ear pain or pressure if the swelling obstructs the ear’s drainage system.
4. Ear Infections
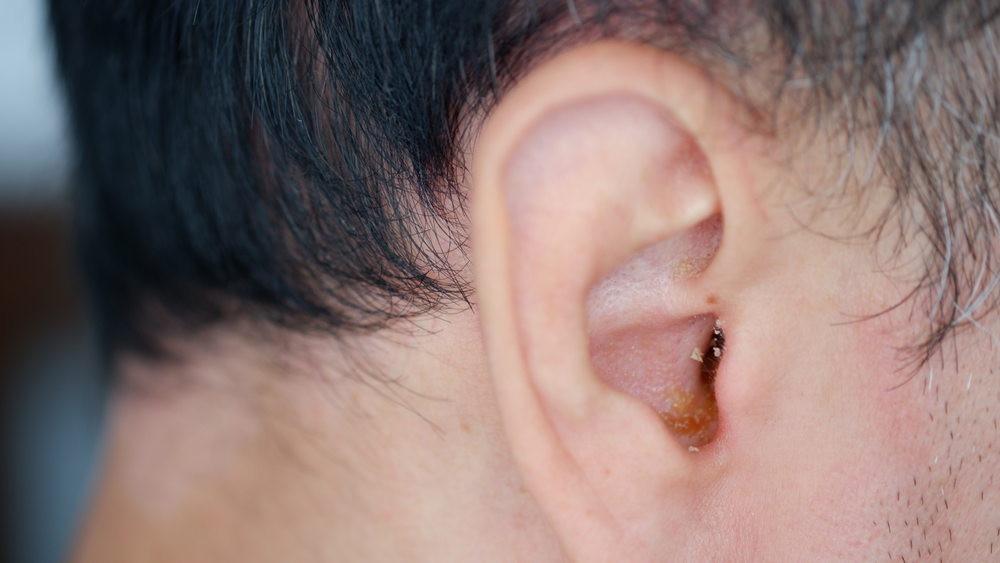
Ear infections are among the most frequent causes of ear pain, particularly in children. These frequently occur when fluid accumulates behind the eardrum. In addition to the pain, you may experience muffled hearing, ear discharge, or fever.
5. A Ruptured Eardrum

The eardrum is sensitive, and it can hurt if it tears due to an infection, loud noises, or prodding with a cotton swab. Additionally, some people experience sudden hearing loss, buzzing noises, or fluid leaking from the ear. Larger ruptures might require medical attention, but smaller ones usually heal on their own.
6. Wax Buildup
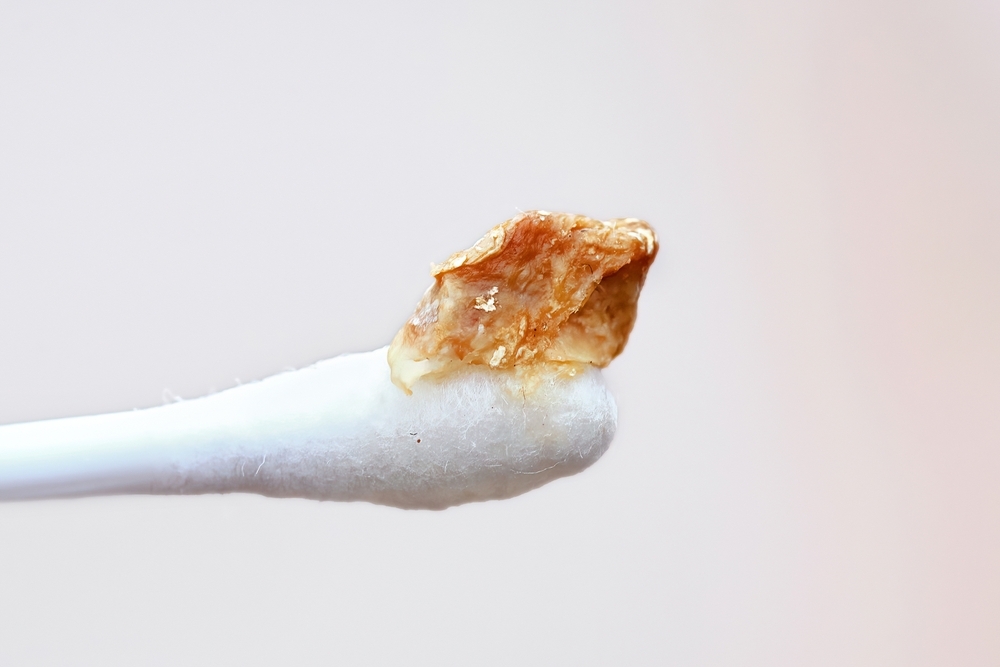

Although too much earwax can obstruct the canal, it is helpful for protecting the ear. Pressure, ringing, dizziness, muffled hearing, and occasionally pain are the results. Fortunately, earwax is frequently simple to remove or soften at home.
7. Air Pressure Changes
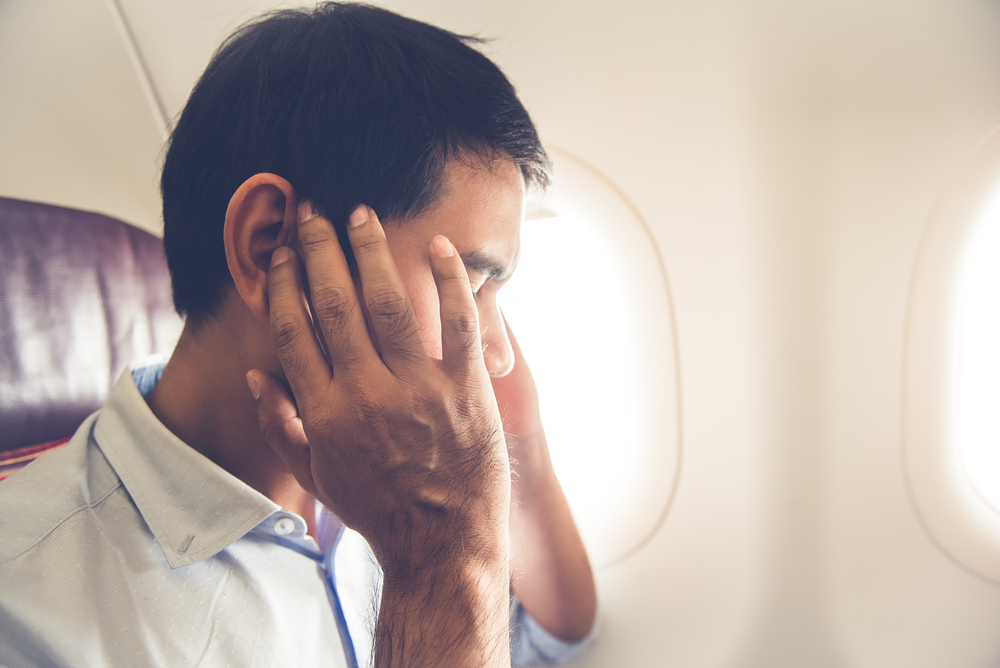

Have you ever had your ears pop while driving up a mountain or flying? When the air pressure inside your ear differs from the pressure outside, it is known as ear barotrauma. Though yawning or swallowing usually helps to balance things out, it can cause pain, stuffiness, and even temporary hearing changes.
8. Swimmer’s Ear

Despite its name, swimmer’s ear is not limited to swimmers. The outer ear may become infected if water or bacteria become lodged in the ear canal. You may experience itching, swelling, or discharge in addition to pain. It usually goes away quickly with prescription ear drops.
9. Jaw Joint Problems (TMD)

Since your jaw joint, also known as the temporomandibular joint, is located near your ears, any problems with it, such as clenching, grinding, or stiffness, can cause pain that travels directly to your ears. Additionally, you may notice your jaw locking or clicking.
10. Tonsillitis
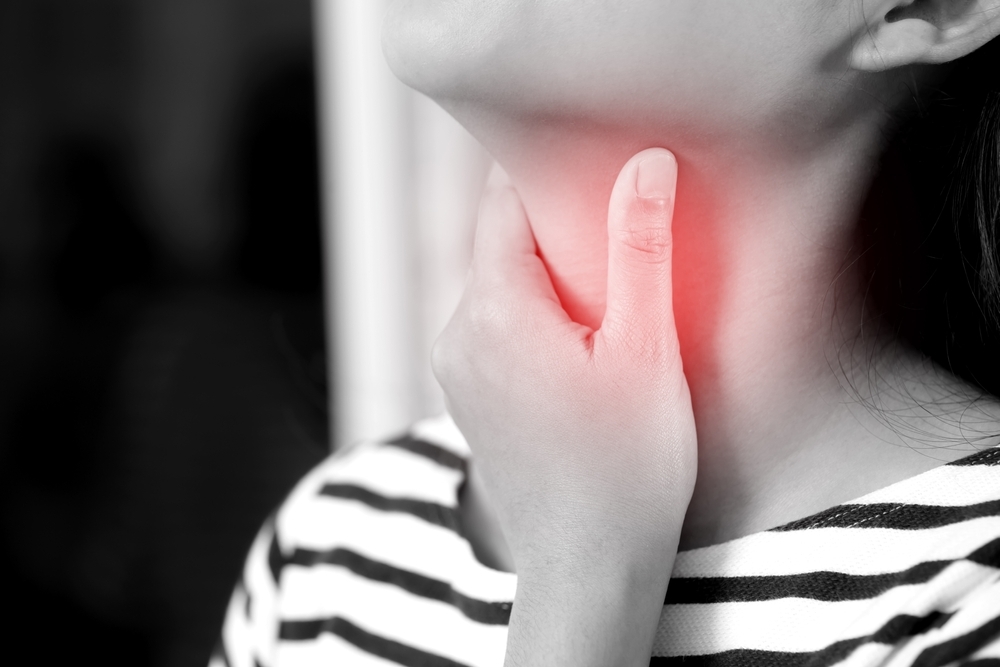
Pain that travels to the ears can be caused by swollen tonsils from infections like strep throat. Inflamed tonsils may be the cause of your sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and ear pain.
Easing the Ache

Home remedies can provide relief for a variety of ear pain causes. For mild discomfort, try taking over-the-counter pain relievers, applying a warm compress for pressure, or chewing gum during flights. Your doctor can assist if earwax is difficult to remove, but it can usually be controlled with drops or mild softening oils.
When to Call a Healthcare Provider
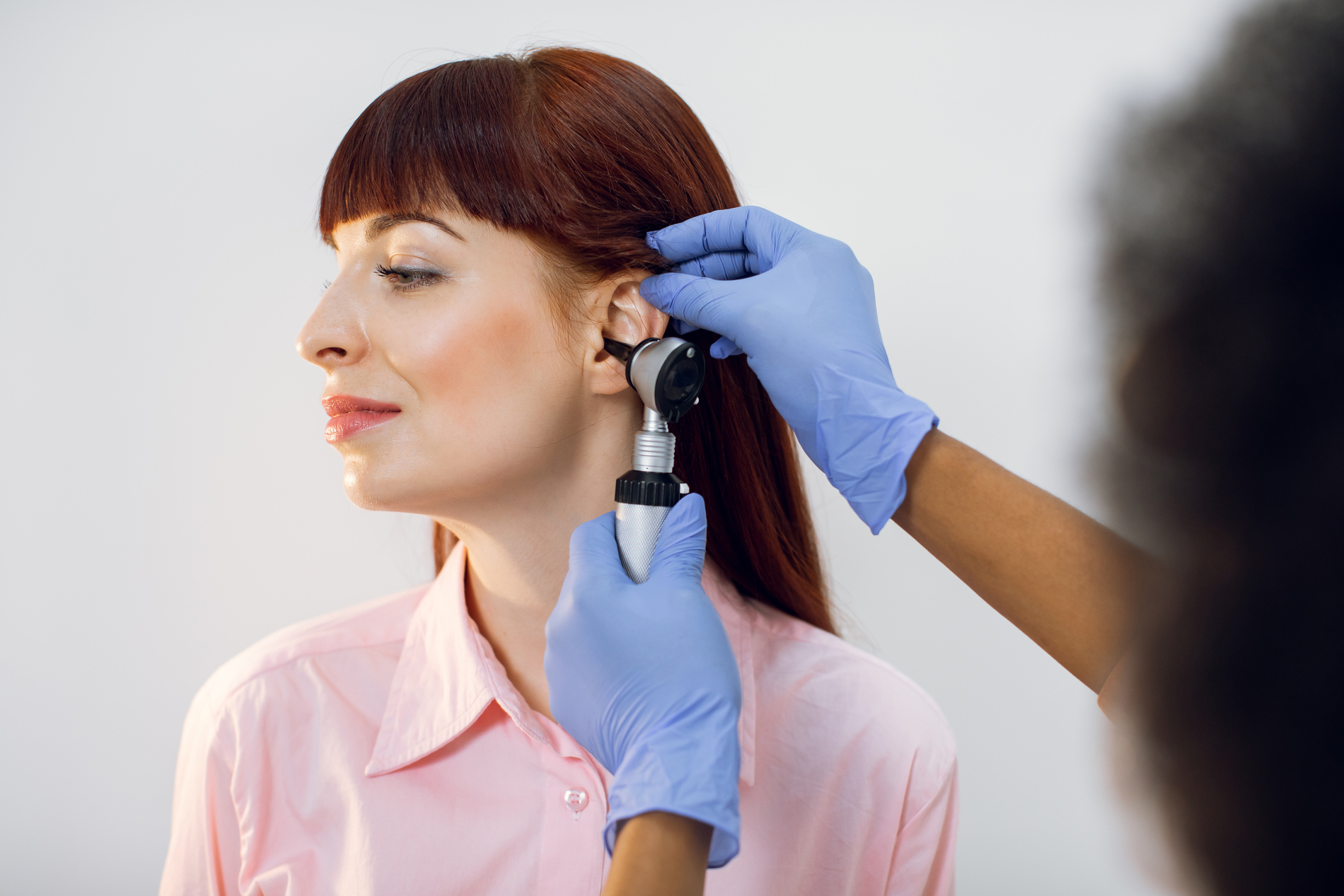
Earaches can occasionally indicate that you need medical help. Consult a specialist if you observe:
- Abrupt relief following excruciating pain (possible rupture of the eardrum)
- Swelling, increasing pain, or fever
- Ear bleeding or discharge
- Hearing loss, dizziness, or new headaches
Keeping Ear Pain Away

Treatment is frequently more difficult than prevention. Avoid sticking objects—including cotton swabs—into your ears, dry your ears after swimming, and use antihistamines or sprays to treat allergies. Earplugs or a mild alcohol-vinegar rinse after swimming may be helpful if you are prone to swimmer’s ear.
Simple causes of ear pain include allergies or wax accumulation, while more complicated causes include infections or problems with the jaw. Home care can usually manage it, but it’s always advisable to get checked out if the pain is severe or persistent. You can avoid pain by taking good care of your ears and avoiding the temptation to prod them.




